Image Credit: iStock Image
Transdermal patches have revolutionized the way medications are delivered, offering a convenient and effective alternative to traditional oral drugs. These innovative medical devices adhere to the skin, allowing controlled release of medication directly into the bloodstream. Transdermal patches have gained popularity for various uses, including pain relief, nicotine replacement therapy, and hormone treatments.
Applying a transdermal patch correctly is crucial to maximize its benefits and minimize side effects. This guide explores how to choose the right patch, ensure proper application, and troubleshoot common issues. Whether you’re using a buprenorphine patch for pain management, a nicotine patch to quit smoking, or a hyoscine patch for motion sickness, understanding the ins and outs of transdermal drug delivery can help you get the most out of this modern medical technology.
Read More About: Peptides For Skin
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing the Right Transdermal Patch
Selecting the appropriate transdermal patch involves considering several factors. The drug’s properties, such as molecular weight and lipophilicity, play a crucial role in determining the patch design. Patients should carefully read the instructions provided with their patch, which specify where to place it, how long to wear it, and when to replace it.
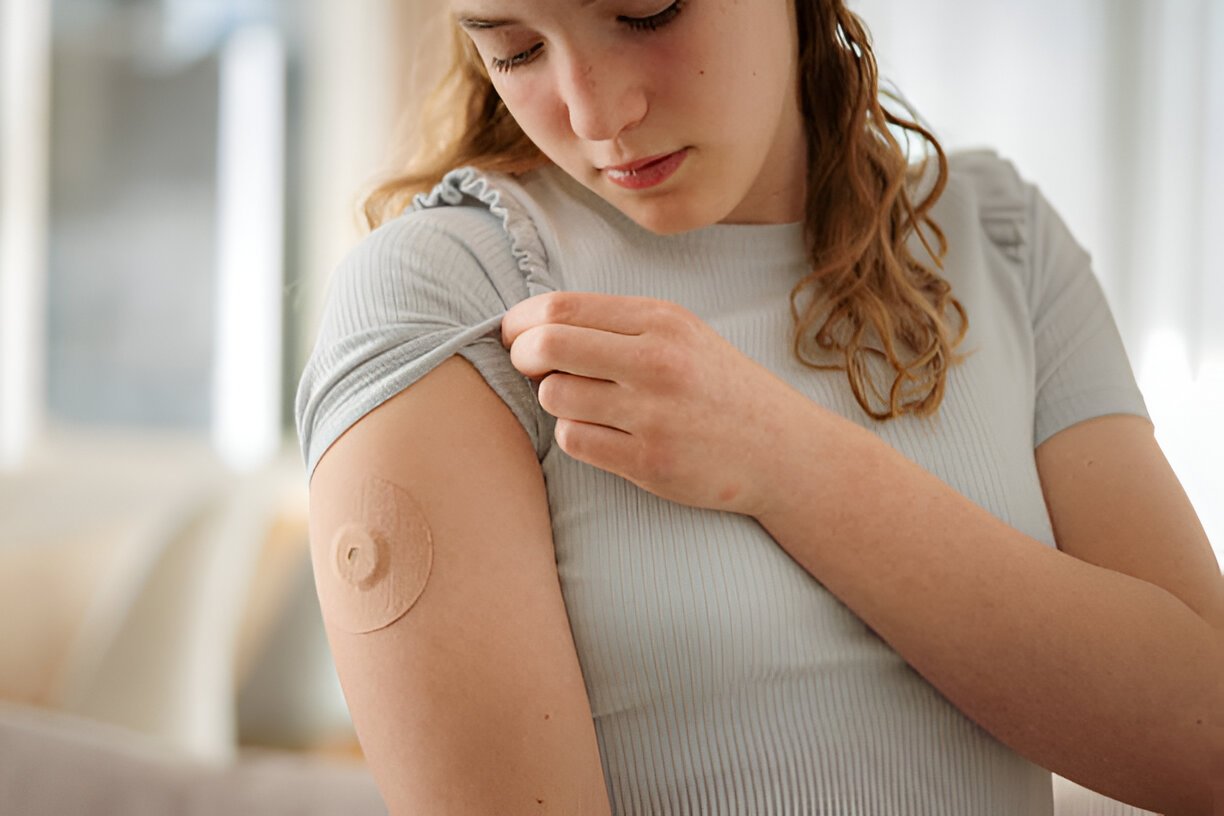
The patch’s location on the body is essential. Some patches are designed for the upper chest or outer arm, while others are meant for the lower abdomen or hip. Skin thickness at the application site can affect drug absorption, potentially leading to side effects or reduced efficacy.
Rotating patch locations within the recommended areas can help prevent skin irritation. When switching between patches, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional about the appropriate interval to avoid toxicity or reduced therapeutic effect.
Patients should also consider the patch’s wear time, which can range from hours to days, depending on the medication. For instance, fentanyl patches are typically worn for 72 hours before replacement.
Maximizing Patch Effectiveness
To get the most out of transdermal patches, proper application is crucial. Users should start by cleaning the application area with clear water, avoiding soaps, oils, or lotions. Once the skin is dry, they can remove the patch from its pouch and peel off the protective liner. The adhesive side should be pressed firmly against the skin for at least 30 seconds, ensuring good contact, especially at the edges. Users should wash their hands after application. When it’s time to change the patch, they should remove the old one, fold it with the adhesive sides together for safe disposal, and apply the new patch to a different area to prevent skin irritation. Rotating application sites within the recommended areas helps maintain effectiveness and minimize skin reactions.
Click Here to Understand About: Cancer Skin Rash
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Users of transdermal patches may encounter several common issues. If a patch doesn’t stick well, they can tape the edges with first-aid tape. For persistent adhesion problems, covering the patch with Bioclusive or Askina Derm brand see-through dressings is recommended. However, other types of bandages or tape should be avoided. If a patch falls off prematurely, users should dispose of it properly and apply a new one to a different skin area, informing their doctor of the incident.
To prevent skin irritation, users should rotate application sites daily and remove patches carefully. Moisturizers and gentle cleansing can help maintain skin health. In case of suspected skin reactions, immediate evaluation by a dermatologist is crucial.
It’s important to note that patches exposed to extreme heat may release too much medication, potentially causing serious symptoms. Users should avoid direct heat sources and activities that may lead to overheating while wearing the patch.
Also Read About to Understand: Skyrizi Side Effects
Conclusion
Transdermal patches have brought about a revolution in medication delivery, offering a user-friendly and effective alternative to traditional oral drugs. These innovative medical devices stick to the skin, allowing for controlled release of medication directly into the bloodstream. By understanding how to choose the right patch, apply it correctly, and troubleshoot common issues, users can make the most of this modern medical technology. Proper application, including cleaning the skin and securing the patch firmly, is key to getting the full benefits.
To wrap up, transdermal patches have a significant impact on various treatments, from pain management to smoking cessation and motion sickness prevention. While they offer many advantages, users should be aware of potential challenges like adhesion problems or skin irritation. By following the guidelines for application, maintenance, and troubleshooting, patients can enjoy the convenience and effectiveness of transdermal drug delivery while minimizing potential side effects. This technology continues to evolve, promising even more breakthroughs in medication administration in the future.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using transdermal patches?
Transdermal patches offer several advantages including bypassing the gastrointestinal system, which helps prevent potential stomach damage from oral medications. These patches also promote consistent usage due to their ease of application and ability to provide a steady release of medication over time. They are a non-invasive alternative to oral medications, often leading to better patient compliance due to their convenience and the avoidance of the first-pass effect in the liver.
How do transdermal patches enhance patient compliance and convenience?
Transdermal patches are straightforward to use, allowing patients to self-administer their medication which reduces the need for frequent medical visits. This self-administration capability encourages patients to adhere more closely to their treatment plans, enhancing the effectiveness of the therapy.
What should nurses consider when applying transdermal patches?
When applying transdermal patches, nurses should ensure privacy and perform hand hygiene before beginning. It is important to wear gloves, remove any previous patch according to the facility’s policy, and choose a new, flat application site such as the chest, back, flank, or upper arm to place the new patch. Explaining the procedure to the patient is also crucial for comfort and compliance.


Leave a Reply